Abstract
We introduce NewsTweet, a dataset and data collection pipeline designed to study the embedding of social media in digital journalism. Our descriptive analysis of articles collected from Google News (chosen for its significant role in shaping attention) reveals that 13% of stories include embedded tweets. The dataset provides a foundation for exploring how social media content is sourced and which users become newsworthy.
Key Contributions
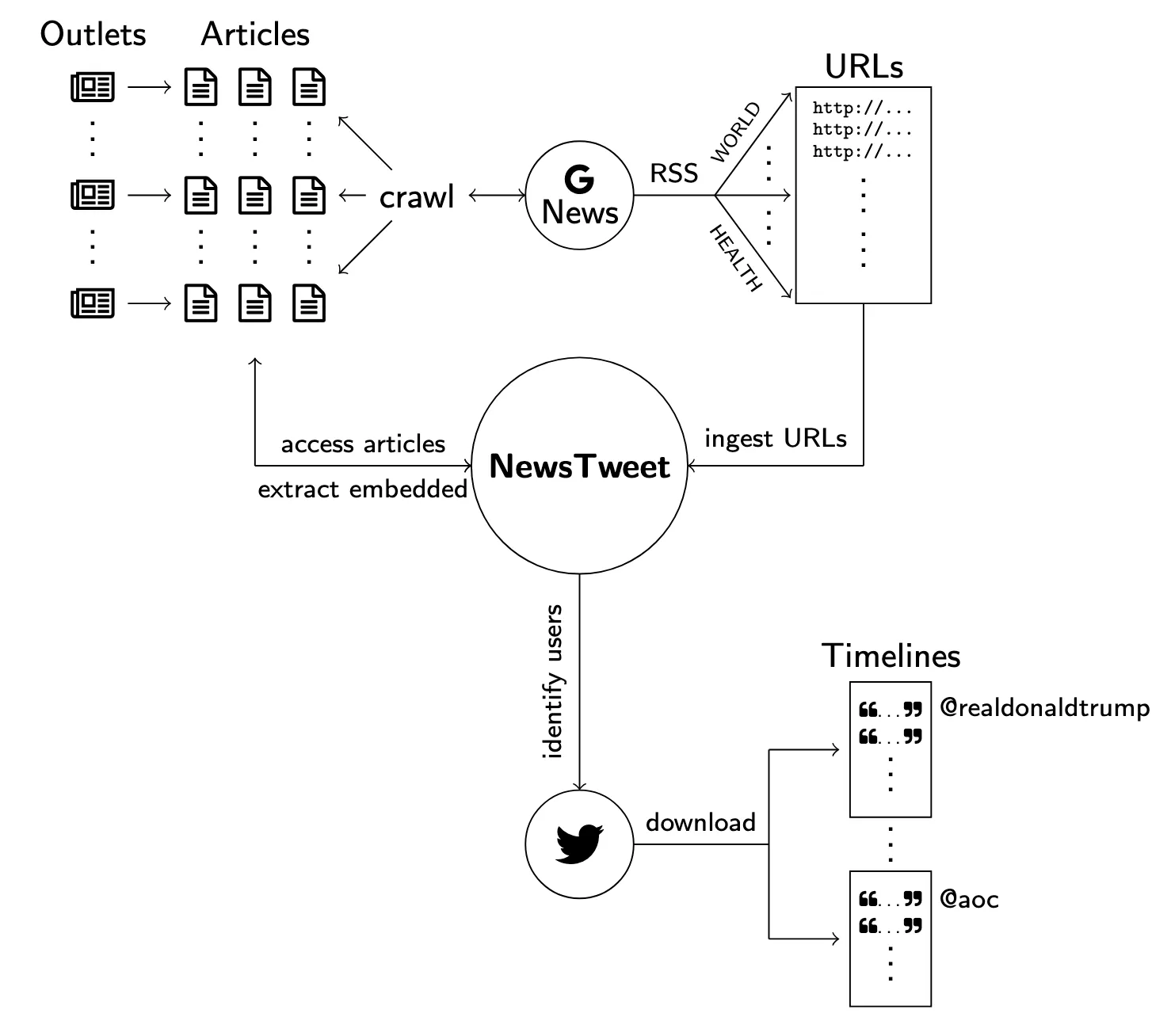
- Large-Scale Dataset: A dataset of 273,899 news articles, with 35,218 containing embedded tweets, collected from Google News RSS feeds over a four-month period.
- Data Collection Pipeline: Details an automated pipeline for acquiring news articles, extracting embedded tweets, and collecting the corresponding user timelines from Twitter’s API.
- Descriptive Statistics: Presents statistics on the prevalence of tweet embedding across different news categories, outlets, and users, highlighting key patterns.
Dataset Characteristics
Scale and Coverage
- News Sources: 5,961 unique news domains aggregated through Google News RSS feeds.
- Time Period: Data collection initiated on May 15th, 2019, with the paper describing the first four months of data.
- Collection Velocity: The pipeline averaged 2,302 articles per day, with approximately 296 containing embedded tweets.
- Content Types: Focuses specifically on embedded tweets from Twitter, the most frequently embedded platform.
- Metadata: Includes article source, Google News category (e.g., Sports, Health), and full tweet and user objects from the Twitter API.
Technical Implementation
- RSS-to-API Pipeline: Automatically crawls Google News RSS feeds to extract article HTML, identifying embedded tweet IDs to fetch full objects via the Twitter API.
- Smart Filtering: Implements cleaning protocols to handle artifacts, such as detecting and excluding YouTube pages that appear as articles in Google News feeds.
- Longitudinal Tracking: Features a “top-off” mechanism that continuously tracks discovered users, updating their timelines to capture historical context.
- Rate Limit Management: Utilizes a random sampling queue to maintain continuous data collection across thousands of users without exceeding Twitter API limits.
Key Findings
Embedding Prevalence
- 13% of news articles in our Google News-sourced collection contained embedded tweets.
- Significant variation across categories: Sports (24% of articles) and Entertainment (14%) had the highest rates of embedding, while Health (2%) had the lowest.
- News outlets that publish the most articles are well-known mass media organizations, while outlets with the highest average number of embeds per article are often focused on Sports and Entertainment.
User and Content Patterns
- Public figures dominate: Well-known figures like politicians and celebrities, alongside organizations, are embedded far more often than ordinary users.
- Some users have a small number of their tweets embedded many times, while others gain newsworthiness from a wider range of their content.
- The Health category, despite having few embedded tweets, had the highest proportion of unique tweets (93%), suggesting that when tweets are embedded, they are less likely to be reused across multiple stories.
- “Catch-up” Phenomenon: Data reveals a class of users with high “embedding effectiveness”: those embedded more frequently than they tweet. This suggests journalists often use embeddings to “catch readers up” on backstories for previously unknown individuals.
Societal Impact
This work provides a foundational dataset for researchers to investigate how social media is shaping news narratives and public discourse. It enables future studies on journalistic sourcing, the rise of internet celebrities, and the role of user-generated content in the modern media landscape.
Applications
- Journalism Research: Studying how sourcing routines are evolving in the digital age.
- Media Studies: Analyzing the interplay between traditional news outlets and social media platforms.
- Meta-Story Construction: The dataset enables the reconstruction of long-term narratives (e.g., the progression of pandemics) and short-term spikes (e.g., cryptocurrency scams) by correlating news velocity with social media activity.
- Platform Studies: Examining how platform policies and features influence news content.
Citation
@misc{mujib2020newstweetdatasetsocialmedia,
title={NewsTweet: A Dataset of Social Media Embedding in Online Journalism},
author={Munif Ishad Mujib and Hunter Scott Heidenreich and Colin J. Murphy and Giovanni C. Santia and Asta Zelenkauskaite and Jake Ryland Williams},
year={2020},
eprint={2008.02870},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.SI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02870}
}
Related Work
For more on social media data models, see Look, Don’t Tweet: Unified Data Models for Social NLP.