Key Contribution: Scaling Make-on-Demand Libraries
ZINC-22 addresses the critical infrastructure challenges of managing multi-billion-scale libraries of make-on-demand chemical compounds through a federated database architecture, the CartBlanche web interface, and cloud distribution systems that enable modern virtual screening.
Overview
ZINC-22 is a multi-billion scale public database of commercially available chemical compounds designed for virtual screening. It contains over 37 billion make-on-demand molecules and utilizes a distributed infrastructure capable of managing database indexing limits. For structural biology pipelines, it provides 4.5 billion ready-to-dock 3D conformations alongside pre-calculated pH-specific protonation states, tautomers, and AMSOL partial charges.
Dataset Examples
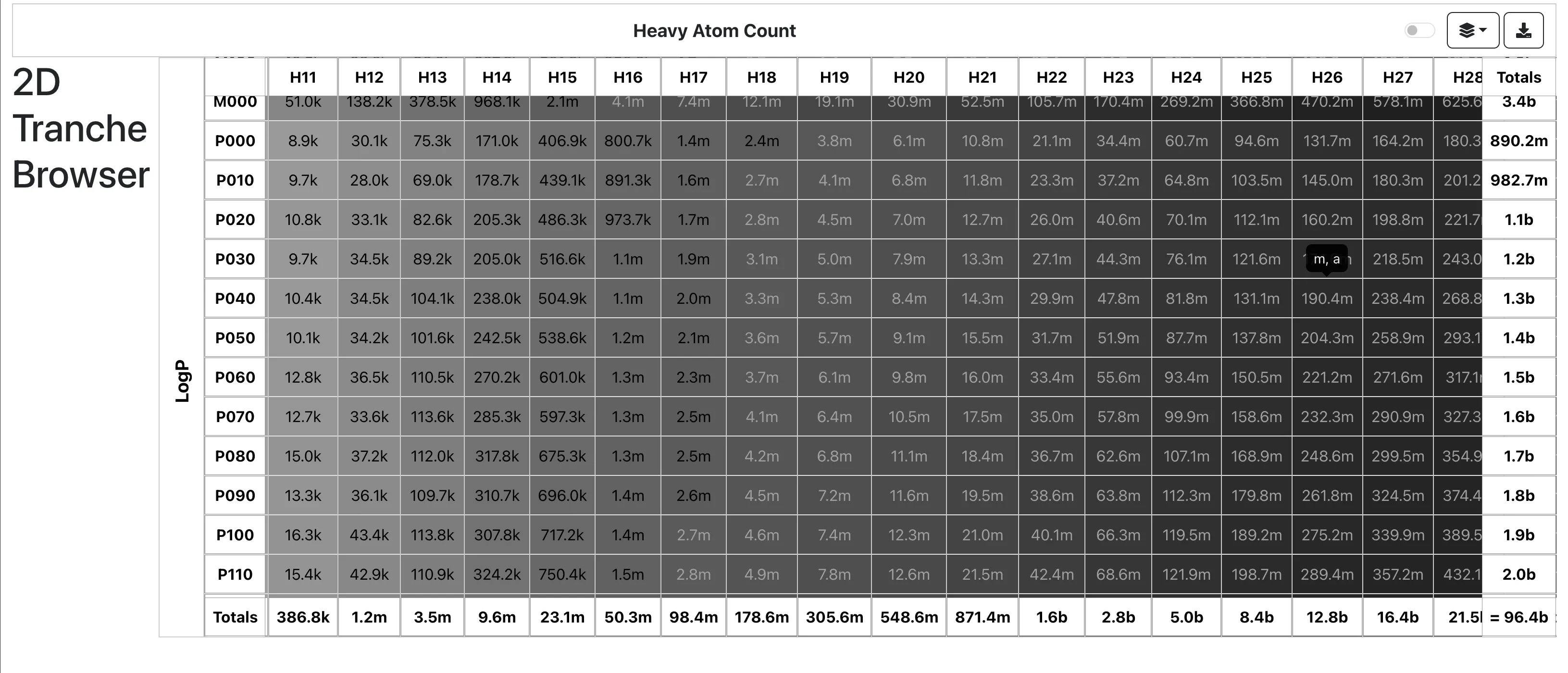
Dataset Subsets
| Subset | Count | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2D Database | 37B+ | Complete 2D chemical structures from make-on-demand catalogs (Enamine, WuXi, Mcule) |
| 3D Database | 4.5B+ | Ready-to-dock 3D conformations with pre-calculated charges and solvation energies |
| Custom Tranches | Variable | User-selected molecular subsets via Tranche Browser (e.g., lead-like, fragment-like) |
Benchmarks
ZINC-22 serves as foundational validation data for modern ultra-large virtual screening (ULVS) methodologies. Subsets or targeted Tranches are routinely sampled to benchmark generative model novelty (verifying generated molecules map correctly into synthetically accessible space) and to baseline rigid-docking hit rates.
Related Datasets
| Dataset | Relationship | Link |
|---|---|---|
| ZINC-20 | Predecessor | |
| Enamine REAL | Source catalog | |
| WuXi GalaXi | Source catalog |
Strengths
- Massive scale: 37+ billion purchasable compounds from major vendors (Enamine, WuXi, Mcule)
- Federated architecture: Supports asynchronous building and horizontal scaling to trillion-molecule growth
- Platform access: CartBlanche GUI provides a shopping cart metaphor for compound acquisition
- Privacy protection: Dual public/private server clusters protect patentability of undisclosed catalogs
- Chemical diversity: Linear growth (1 new scaffold per 10 molecules added), with 96.3M+ unique Bemis-Murcko scaffolds
- Ready-to-dock: 3D models include pre-calculated charges, protonation states, and solvation energies
- Cloud distribution: Available via AWS Open Data, Oracle OCI, and UCSF servers
- Scale-aware search: SmallWorld (similarity) and Arthor (substructure) tools partitioned to address specific constraints of billion-scale queries
- Organized access: Tranche system enables targeted selection of chemical space
- Open access: Entire database freely available to academic and commercial users
Limitations
- Data Transfer Bottlenecks: Distributing 4.5 billion 3D alignments in standard rigid format (like db2 flexibase) requires roughly 1 Petabyte of storage. Transferring this takes months over standard gigabit connections, effectively mandating cloud-based compilation and rendering local copies impractical.
- Search Result Caps: Interactive Arthor operations are strictly capped at 20,000 hits due to linear processing requirements and server RAM constraints.
- Enumeration Ceiling: Scaling relies entirely on PostgreSQL sharding. To continue using rigid docking tools, the database must fully enumerate structural states. The authors acknowledge that hardware limitations will likely cap full database enumeration well before the 10-trillion molecule mark, forcing future pipelines to accommodate unenumerated combinatorial fragment spaces.
- Download Workflow: Individual 3D molecule downloads are unavailable directly; researchers must rebuild them via the TLDR tool.
- Vendor Updates: There is difficulty removing discontinued vendor molecules due to the federated structure.
Technical Notes
Hardware & Software
Compute infrastructure:
- 1,700 cores across 14 computers for parallel processing
- 174 independent PostgreSQL 12.0 databases (110 ‘Sn’ for ZINC-ID, 64 ‘Sb’ for Supplier Codes)
- Distributed across Amazon AWS, Oracle OCI, and UCSF servers
Software stack:
- PostgreSQL 12.2
- Python 3.6.8
- RDKit 2020.03
- Celery task queue with Redis for background processing
- All code available on GitHub: docking-org/zinc22-2d, zinc22-3d
Data Organization & Access
Tranche system: Molecules organized into “Tranches” based on 4 dimensions:
- Heavy Atom Count
- Lipophilicity (LogP)
- Charge
- File Format
This enables downloading specific chemical neighborhoods (e.g., neutral lead-like molecules) without accessing the entire database.
Search infrastructure: Searching at the billion-molecule scale actively exceeds rapid-access computer memory limits. ZINC-22 splits retrieval between two distinct algorithms:
SmallWorld: Handles whole-molecule similarity using Graph Edit Distance (GED). GED defines the minimum cost of operations (node/edge insertions, deletions, or substitutions) required to transform graph $G_1$ into graph $G_2$:
$$ \text{GED}(G_1, G_2) = \min_{(e_1, …, e_k) \in \mathcal{P}(G_1, G_2)} \sum_{i=1}^k c(e_i) $$
Because SmallWorld searches pre-calculated anonymous graphs, it evaluates close neighbors in near $\mathcal{O}(1)$ time and scales sub-linearly, though it struggles with highly distant structural matches.
Arthor: Provides exact substructure and pattern matching. It scales linearly $\mathcal{O}(N)$ with database size and successfully finds distant hits (e.g., PAINS filters), but performance heavily degrades if the index exceeds available RAM.
CartBlanche: Web interface wrapping these search tools with shopping cart functionality.
3D Generation Pipeline
The 3D database construction pipeline involves multiple specialized tools:
- ChemAxon JChem: Protonation state generation at physiological pH
- Corina: Initial 3D structure generation
- Omega: Conformation sampling
- AMSOL 7.1: Calculation of atomic partial charges and desolvation energies
Chemical Diversity Analysis
A core debate in billion-scale library generation involves whether continuous enumeration merely yields repetitive derivatives. Analysis of Bemis-Murcko (BM) scaffolds demonstrates that chemical diversity in ZINC-22 continues to grow, but scales sub-linearly based on a power law. Specifically, the authors observe a $\log$ increase in BM scaffolds for every two $\log$ increase in database size:
$$ \log(\text{Scaffolds}_{BM}) \propto 0.5 \log(\text{Molecules}) $$
This suggests that while diversity does not saturate, it grows proportionally to the square root of the library size ($\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{N})$). The majority of this scaffold novelty stems from compounds with the highest heavy atom counts (HAC 24-25), which contribute roughly twice as many unique core structures as the combined HAC 06-23 subset.
Vendor Integration
ZINC-22 emphasizes commercially available compounds from large make-on-demand catalogs:
- Enamine REAL: Multi-billion compound virtual library
- WuXi GalaXi: Extensive make-on-demand catalog
- Mcule: Diverse purchasable compound collection
This focus on purchasable molecules distinguishes ZINC-22 from theoretical chemical space databases.
Reproducibility Details
- Data Availability: The compiled database is openly accessible and searchable through the CartBlanche web interface. Subsets can be downloaded, and programmatic access is provided.
- Code & Algorithms: The source code for database construction, parallel processing, and querying is open-source.
- 2D Pipeline: docking-org/zinc22-2d
- 3D Pipeline: docking-org/zinc22-3d
- Software Dependencies: While the orchestration code is public, the 3D structure generation heavily relies on commercial, proprietary software that requires separate licenses (e.g., CORINA, OpenEye OMEGA, ChemAxon JChem). This limits true end-to-end reproducibility for researchers without access to these tools.
- Hardware Limitations: Recreating the entire 37+ billion molecule database from raw vendor catalogs requires thousands of CPU cores and petabytes of data transfer, functionally restricting full recreation to large institutional clusters or substantial cloud compute budgets.
Citation
@article{Tingle_2023,
title={ZINC-22: A Free Multi-Billion-Scale Database of Tangible Compounds for Ligand Discovery},
volume={63},
ISSN={1549-960X},
url={http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.2c01253},
DOI={10.1021/acs.jcim.2c01253},
number={4},
journal={Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling},
publisher={American Chemical Society (ACS)},
author={Tingle, Benjamin I. and Tang, Khanh G. and Castanon, Mar and Gutierrez, John J. and Khurelbaatar, Munkhzul and Dandarchuluun, Chinzorig and Moroz, Yurii S. and Irwin, John J.},
year={2023},
month={Feb},
pages={1166-1176}
}
